
A certificate’s validity typically depends on several factors, including its content, purpose, and the context in which it is issued. A certificate may include a signature, but that alone does not necessarily guarantee its authenticity or validity. The validity of a certificate usually depends on whether:
- It has the proper authority’s signature or digital signature (if it’s an electronically issued certificate).
- It includes the relevant details such as the certificate holder’s name, date of issue, purpose, and any other necessary identifiers.
- It’s issued by a recognized body or authority with the necessary legal backing.
In the case of a digital certificate (such as those issued for secure communications or public key infrastructure), the certificate may include a signature from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA), which ensures its validity.
What is a certificate?
A certificate, in the context you’re asking, is a formal document that attests to a fact, skill, achievement, identity, or qualification. It can serve many purposes, such as verifying someone’s credentials (e.g., educational certificates), confirming compliance with standards (e.g., quality assurance certifications), or ensuring authenticity in digital communications (e.g., SSL/TLS certificates).
Types of Certificates:
- Educational Certificates: Verify qualifications or achievements.
- Professional Certificates: Validate skills or professional standing.
- Digital Certificates: Used for encryption, signing documents, and secure communication (e.g., SSL/TLS, Code Signing).
- Compliance/Regulatory Certificates: For businesses ensuring adherence to regulatory standards.
Best Practices for Issuing a Certificate in India
When issuing certificates in India, especially in formal or legal contexts, the process must follow certain best practices to ensure authenticity, trust, and legal compliance:
- Authority & Verification: Ensure the certificate is issued by a legitimate authority (e.g., an educational institution, government body, professional association).
- Unique Identifier: Include a unique identifier (e.g., certificate number, QR code, etc.) to make verification easy and prevent fraud.
- Digital Security: If the certificate is digital, it should be signed with a secure digital signature. For offline certificates, include features such as embossed seals, signatures, or even holograms to ensure authenticity.
- Date and Details: Clearly specify the date of issue, the recipient’s details, and the purpose of the certificate. This makes it easier to verify the authenticity later.
- Compliance with Laws: Follow Indian regulations such as the Indian Contract Act, Indian Evidence Act, and Information Technology Act (for digital certificates) to ensure that the certificate is legally valid.
- Record Keeping: Maintain a secure record or database of all issued certificates. This is especially important for educational institutions or businesses that issue certificates for compliance or training.
- Online Verification: If issuing digital certificates, enable online verification (such as a verification link or code) so third parties can confirm the certificate’s authenticity.
Can the Same Certificate Be Issued with Only the Date Changed?
In principle, a certificate can be reissued with a new date, but it must be clearly marked or issued as a replacement to avoid confusion. Simply changing the date without following proper reissuance protocols may lead to concerns about authenticity or intent. This is especially true in contexts where the certificate may serve as a legal document or a qualification.
In the case of digital certificates (e.g., SSL certificates), changing the date could also involve regenerating the cryptographic components of the certificate, and simply changing the date might invalidate the signature or make the certificate technically incorrect.
If the certificate is a physical document, reissuing a certificate with a new date can raise questions unless it’s done under clear and proper processes (e.g., correcting an error in the original issue).
Best practices for changing the date:
- Reissue with New Serial Number or Identifier: The certificate should have a new serial number, especially if it replaces an earlier version.
- Document the Reason: Always document why the date is being changed, especially in official contexts (e.g., academic certificates or professional certifications).
- Communicate the Change Clearly: Inform relevant stakeholders (such as the recipient or any entity relying on the certificate) about the change to avoid confusion.
Validity of general cirtificates
A certificate’s validity is determined by various factors, not just the signature. A certificate is a formal document that verifies specific information or qualifications. Best practices for issuing certificates in India include ensuring authority, clear documentation, and appropriate security features. Changing only the date on an existing certificate may be possible, but it should be done with care and transparency to ensure that the certificate remains valid and trustworthy.
In recent times, numerous online educational platforms and schools have emerged, offering a wide range of certifications in various fields. One such certification is the LokNeeti certificate, which is issued by a relatively unknown entity called the Dizital Azadi School. Despite the increasing popularity of this certificate among thousands of students across India, questions regarding its authenticity and credibility remain a matter of concern.
Overview of the LokNeeti Certificate
The LokNeeti certificate, as per claims, is awarded by the Dizital Azadi School to students who complete certain online courses or training programs. The certificate is presented as a recognition of the students’ achievements or participation in courses related to digital marketing. However, despite its widespread circulation, the certificate’s legitimacy and its potential use in academic or professional contexts have raised important questions.
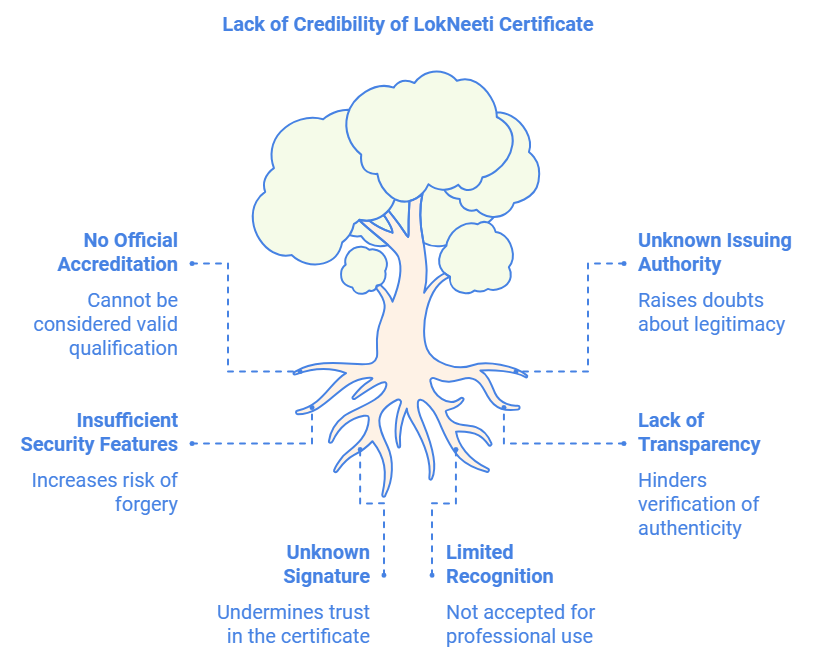
Lack of Recognized Accreditation
One of the primary concerns surrounding the LokNeeti certificate is the lack of official recognition or accreditation from any recognized educational body, government institution, or industry standard. In India, educational certificates typically need to be accredited by the concerned authority or an appropriate professional body in order to be considered valid and legitimate. Without official endorsement, the certificate cannot be considered as a valid qualification for professional purposes.
Absence of Clear Identity and Transparency
Another significant issue with the LokNeeti certificate is the lack of transparency regarding the organization issuing it. The Dizital Azadi School remains largely unknown in the public domain, and there is little to no verifiable information available about it. This absence of clarity regarding the institution’s legitimacy is a major red flag when evaluating the authenticity of the certificate.
Moreover, the certificate itself is said to carry only an “unknown signature,” which raises further doubts about the authority behind its issuance. Authentic certifications from reputable institutions usually include details such as signatures from recognized officials, institutional logos, and sometimes even verification QR codes or holograms to prevent forgery. The LokNeeti certificate’s lack of these basic security features further diminishes its credibility.
LokNeeti certificate Conclusion
While the LokNeeti certificate may serve as a recognition of participation in an online course, it is important to understand that it lacks the official validation required to be considered a legitimate qualification. The absence of proper accreditation, transparency, and secure authentication mechanisms renders the LokNeeti certificate inauthentic for any formal or official use. Students and professionals should exercise caution and verify the legitimacy of any certification before relying on it for career advancement or further education.
The LokNeeti certificate issued by Dizital Azadi School, bearing only an unknown signature, lacks official accreditation and recognized authority. While it is distributed to thousands of students across India, it cannot be considered an authentic or valid qualification for employment or further education. The certificate should be viewed solely as evidence of participation in a course, rather than a credential with formal academic or professional value. Without proper validation, security features, or transparency about the issuing institution, the LokNeeti certificate holds no official standing and cannot be used to prove expertise or achievement in a specific field.
